Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Relative atomic mass (Ar) & atomic mass unit (amu)
- Average atomic mass
- Relative molecular mass (Mr)
- Formula unit & relative formula mass of ionic compounds
Relative Atomic Mass (Ar):
Definition: “The masses of atoms are compared with the mass of carbon-12”, are called relative atomic masses.
Carbon-12 isotope is considered the standard reference to compare atomic masses of the atoms either lighter or heavier. C-12 contains 6 protons plus 6 neutrons in its nucleus. So, it defines the term ‘atomic mass unit’ (amu). One amu equals to 1/12th of C-12. In other words, one amu equals to the mass of a proton or neutron, i.e., 1.67×10-27kg.
The formula for measuring relative atomic masses is as under:
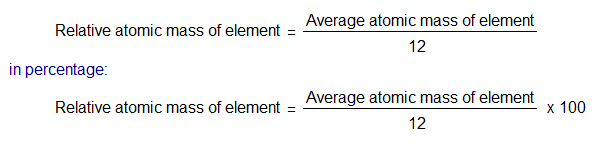
Relevance of atomic masses of various elements with C-12 is as under:
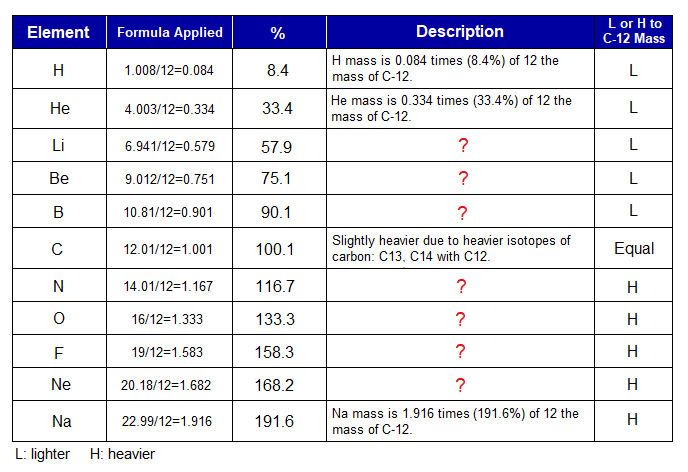
In another view, the value how many times of 12 if multiplied by 12, can calculate in reverse the average mass of that element. For example, if 1.333 of oxygen is multiplied by 12, then, ~ 16 is obtained. Likewise, for all other examples.
Relative atomic mass is a ratio of atomic mass of an element with 12amu of C-12. For example, 1.333 is quotient of 16/12 for oxygen. O-16 means 16amu; it is heavier to 12amu of C-12 and having a ratio of 4:3 for 16:12.
Exercise 1:
- An element has its atomic mass two times heavier than C-12. Find out the element.
- An element has its atomic mass three times heavier than C-12. Find out the element.
Average Atomic Mass:
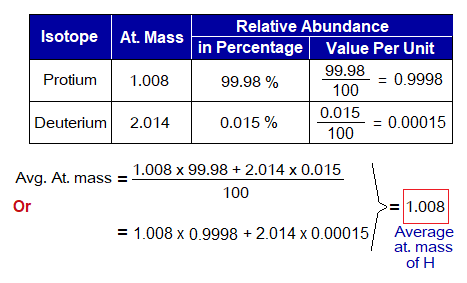
It is defined as“the arithmetic average of masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element with respect to percentages of their relative abundances” is called average atomic mass of an element. For calculation, the relative abundance of an isotope is multiplied by its atomic mass; so is the mathematical procedure for all isotopes of that element. Then, the answers are sum up and divided by 100 to get average atomic mass of the element. The relative abundance is a percentage number; so, the value is divided to get decimal or fractional value to normalize the number. In other words, the value in 100 parts is converted into 1 part.

The average atomic mass of hydrogen atom is calculated as under:
Exercise 2:
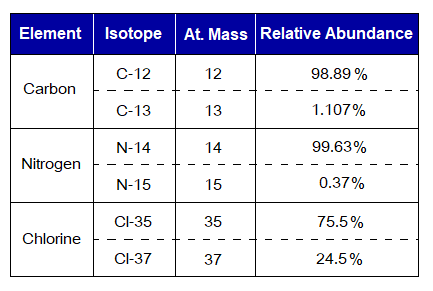
Calculate average atomic masses of C, N & Cl from the data given in the following table.
Relative Molecular Mass (Mr):
It is defined as, “the sum of relative atomic masses of all the atoms present in that molecule”.

Formula Unit:
Molecules of ionic compounds are called formula unit. Because, these are cluster of cations and anions held together by strong electrostatic forces of attractions; and form three-dimensional lattice rather than a separate discrete molecule as in covalent bonds. The simplest whole number ratio between cations and anions is in actual fact the formula unit.
Like, covalent molecules, the Mr is calculated on the same pattern but is called relative formula mass of ionic compounds. Few examples are given below:

Exercise 3:
Calculate Mr for the compounds, CH3COOH, HCl, NaBr, KCl, CaO, NH3, CH4, C2H6, ZnS. Ar of Br:80; C:12; Ca:40; Cl:35.5; H:1; K:39; N:14; O:16; S:32; Zn:65.