Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Melting and boiling points
- Electrical conductivity
Melting & Boiling Points:
The simple covalent molecules have very low melting and boiling points.
There are two types of forces in the compounds:
- Intra-molecular: within a molecule, like covalent bond, ionic bond
- Intermolecular: between molecules
Intermolecular forces are always weak as compared to intra-molecular. In simple covalent molecules these are much weaker; so, causing the melting and boiling points lower. Intermolecular forces are shown always by dotted lines. Following diagram shows the forces between and within molecules of water. In water, the intermolecular forces exist between oxygen of one molecule and the hydrogen of another nearby molecule. These are temporary forces and all the time keep forming and breaking between molecules.
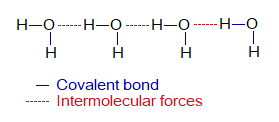
Simple covalent molecules have their individual molecular existence i.e., they are independent. In other words, they don’t exist in the form of cluster like ionic compounds. The ionic compounds are the cluster of ions. Further, simple covalent molecules are not giant structures like diamond. So, their melting and boiling points are very low.
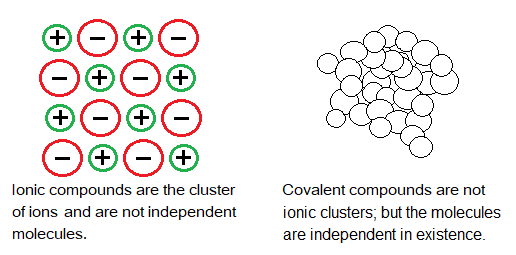
The reasons of low values for such compounds can be summarized as:
- having weak intermolecular forces,
- smaller molecular size,
- non-ionic compounds and the molecules have their independent existence.
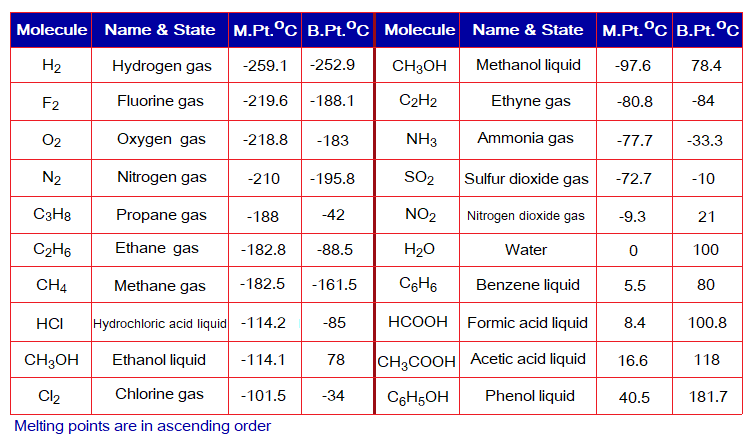
Following table shows that most of the melting and boiling points are below 100 degrees Celsius, or even below zero. Look over the following examples just to know that most covalently bonded simple compounds are gases at room temperature.
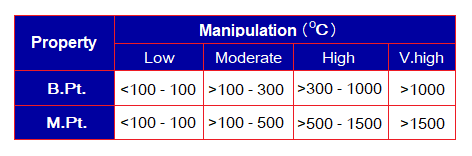
The following table manipulates a general parameter to classify melting and boiling points as low, moderate, or high. It can also be seen in the link: https://chemiologist.com/properties-of-ionic-compounds/
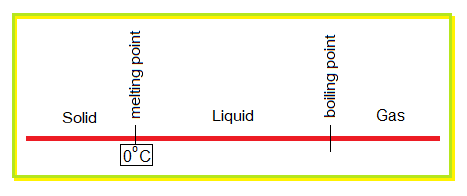
Exercise 1:
Using the following diagram and the above examples given in the table, determine the compounds exist in liquid state between the temperature 10°C to 45°C of the atmosphere.
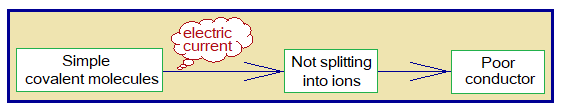
Electrical Conductivity:
Unlike ionic compounds, these are poor conductor of electricity due to the reason of non-ionic nature, in either state, gaseous, molten or solid.
I am glad to be one of the visitants on this outstanding site (:, appreciate it for posting.