Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Higher Education Department, Govt. of the Punjab, Pakistan.
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition
- Modified form of aldol condensation
- Overall reaction
- Mechanism
Definition:
It is a condensation of aldehyde or ketone with an active methylene compound initially in the presence of a base as catalyst, then, forming alpha-beta unsaturation between carbons by dehydration in acidic media.
Modified form of Aldol Condensation:
Knoevenagel reaction is a modified form of aldol condensation, as a double bond is formed between two carbons at the end with the elimination of water molecule. However, in simple aldol, the carbonyl and hydroxyl groups and no unsaturation exist. This reaction was developed by a German chemist, Heinrich Emil Albert Knoevenagel (1865-1921).
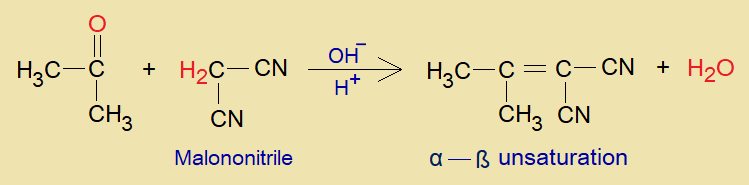
Overall Reaction:
Suppose, malononitrile is taken as active methylene compound that reacts with propanone (acetone) in the presence of a base. Ultimately, a compound is formed containing alpha-beta unsaturation between two carbons by means of dehydration.
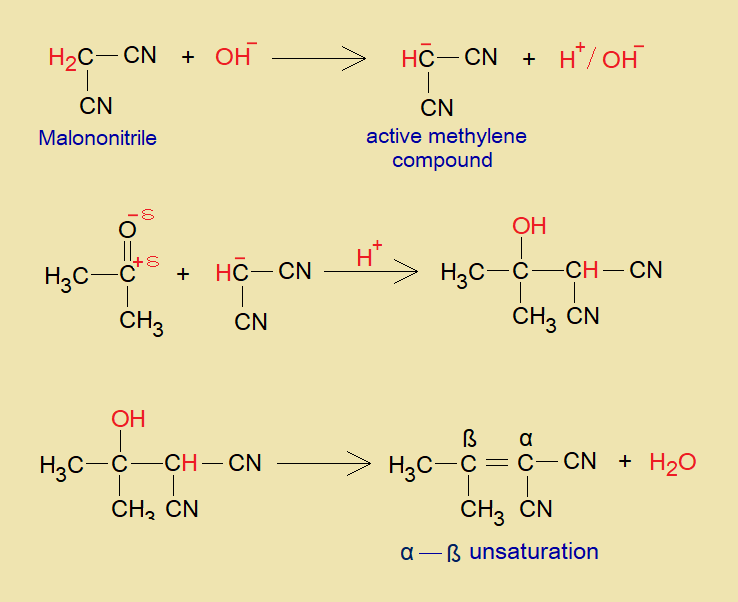
Mechanism:
The mechanism is base catalyzed. The hydroxide ion of base makes water by removing proton from methylene and consequently, carbanion is produced as an active methylene. In acidic media, this carbanion attacks on partial positive carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone, and makes a c-c bond. Then, ultimately, the dehydration occurs and alpha-beta unsaturation is formed by c-c double bond as a final product.