Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Definitions and etymology of isotopes
- Isotopes of hydrogen element
- Isotopes of carbon element
- Calculation of number of neutrons in an isotope
- Isotopes of chlorine element
- Average atomic mass and its calculation
- Symbolization
- Use of mass spectrometer
Definitions of Isotopes:
- The atoms of the same element having different number of neutrons are called isotopes.
- The atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different atomic masses are called isotopes.
Etymology: Origin of the term‘isotope’ is Greek ‘isos’ plus ‘topos’; meanings ‘same or equal’ and ‘place’ respectively. So, isotope means ‘the same place’. All isotopes of an element given the same place (box) in the periodic table. Because, modern periodic table is based upon ‘atomic numbers’, rather than ‘atomic mass’. And according to definition, isotopes of the same element don’t differ from one another with respect to atomic number. All the isotopes of hydrogen are considered to be placed in green box rather than elsewhere in separate box. Likewise, for all other cases, for example isotopes of oxygen have their same place in yellow box. Consider for N & C as well.
It would not be wrong to say that isotopes are not considered in modern periodic table; because, the table was not constructed based on atomic masses.
Isotopes of Hydrogen Element:
Hydrogen element is consisted of three types of isotopes:
- Protium
- Deuterium
- Tritium
Look at the structures of the isotopes below; all the three have same number of electrons and protons (p); but having neutron (n) number different. Protium is yet the only known atom without neutron. Deuterium carries 1 while tritium 2 neutrons in their nucleus.
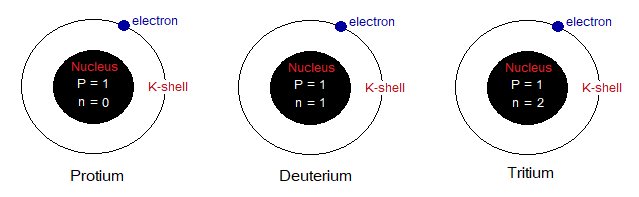
Now, come to calculate their atomic numbers and atomic masses. As the atomic number of an atom is the sum of numbers of protons; so, each of them has atomic number of 1. The atomic mass is the sum of numbers of protons and neutrons; so, all isotopes are different from one another in this feature. Following table helps how to calculate atomic masses, protium has 1, deuterium 2 and tritium 3. So, protium is lightest isotope, deuterium in the middle, while tritium is heavier one.

Isotopes of Carbon Element:
The carbon element exists in three isotopic forms, listed below:
- Carbon-12
- Carbon-13
- Carbon-14
Now, look at the details given in the table below.
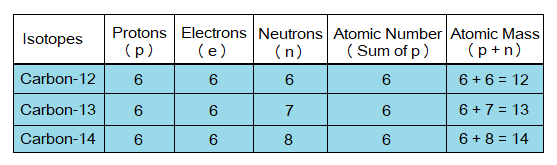
Exercise 1:
- Study the table above for carbon isotopes and go through structural details and features of isotopes.
- Also, come to know the heavier, middle and lighter isotopes on the basis of atomic masses.
Calculation of Number of Neutrons in an Isotope:
By subtracting atomic number (Z) from atomic mass (A) calculates the number of neutrons. For example:
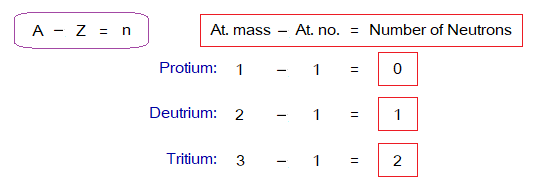
Exercise 2:
Calculate the number of neutrons for three isotopes of carbon by using the above formula. And verify the correctness of your answers using the table above related to carbon isotopes.
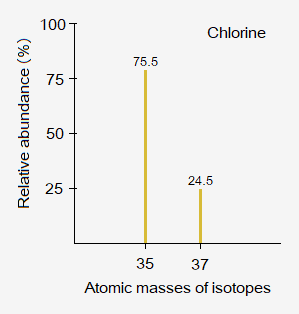
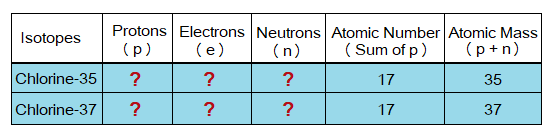
Isotopes of Chlorine Element:
Naturally, chlorine element is consisted of two stable isotopes:
- Chlorine-35
- Chlorine-37
Exercise 3:
Based on the above information, fill in the boxes of the table below that contain red question marks.
Symbolization:
The link https://chemiologist.com/neutrons-atomic-mass-mendeleev-periodic-table-foundational-principles/ describes how to symbolize the element with its atomic number and atomic mass. Z is the symbol for atomic number; A is the symbol for atomic mass. Suppose, if E is taken here as a symbol of an element, then, it can be expressed by the way shown in the following table.
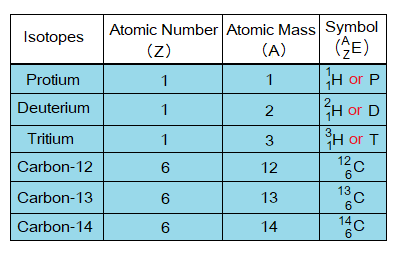
Exercise 4:
Write symbolic forms of both the isotopes of chlorine.
Average Atomic Mass:
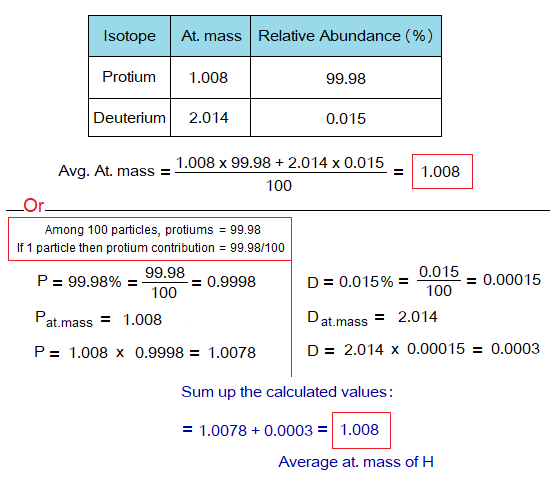
Because, elements are consisted of isotopes, so, their average atomic masses are calculated. The atomic masses seen in fractions are due to this reason. The formula is simple, as the atomic mass of each isotope is multiplied by its relative abundance, and the products of multiplications are summed up to get the total. The total is then divided by 100 to calculate average atomic mass.
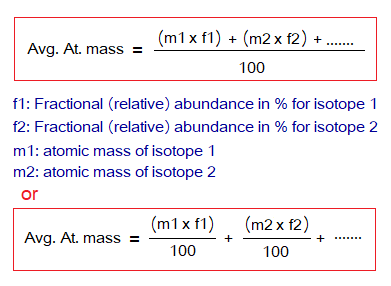
Calculation of Average At. Mass of Hydrogen:
Naturally, protium and deuterium are isotopes of hydrogen; tritium is artificially generated. So, using P & D, the average atomic mass is calculated from the data as given in the table.
Exercise 5:
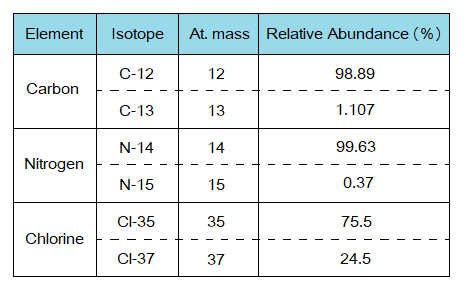
By using the data of the following table, calculate average atomic masses for C. N and Cl.
Use of Mass Spectrometer:
Mass spectrometer is an instrument that is used to determine masses of isotopes and their relative abundances in percentages in the sample and show the data in graph called mass spectrogram (aka mass spectrum) as shown below for chlorine-35 & 37.