Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Groups’ numbers and names
- Periods’ numbers
Groups’ Numbers and Names:
- By definition, the groups are the vertical columns of the periodic table; and containing elements in ascending order of their atomic numbers. The vertical columns are top to bottom arrangement of elements.
- The elements of one group are similar in physical and chemical properties.
- The periodic table is divided into two major blocks, A and B. The A-block is consisted of 8 groups (IA to VIIIA, the white boxes in the figure below). The B-block also consisted of 8 groups (IB to VIIIB the yellow boxes).
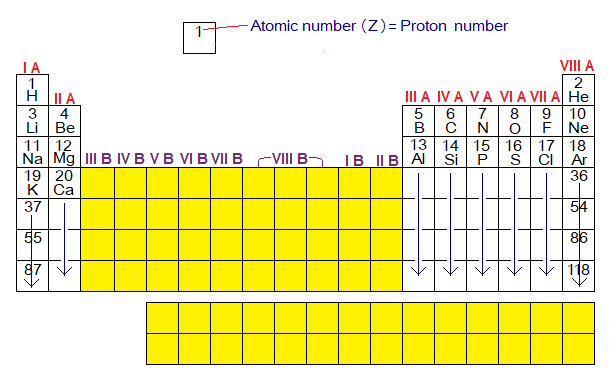
- For A-block, the group number is also related with the electrons in outermost shells of the elements. Mostly, the group number is written by Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, & VIII); however, natural numbers are also used, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 & 8 respectively. The details of the relationships between group numbers and electrons in OMSs is as under:
1A: H, Li, Na, K, and others carry 1 electron in OMS, and belongs to 1A.
2A: Be, Mg, Ca, and others carry 2 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 2A.
3A: B, Al and others carry 3 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 3A.
4A: C, Si and others carry 4 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 4A.
5A: N, P and others carry 5 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 5A.
6A: O, S and others carry 6 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 6A.
7A: F, Cl, Br, and others carry 7 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 7A.
8A: Helium is exceptional case; but Ne, Ar and others carry 8 electrons in OMS, and belongs to 8A.
For A-block, the group number corresponds to the number of electrons in OMS is shown below in a table:

- All groups are recognized not only by their particular number, but also by their specific name, as under:
- 1A: Alkali metals
- 2A: Alkaline Earth metals
- 3A: Boron family
- 4A: Carbon family
- 5A: Nitrogen family
- 6A: Oxygen family
- 7A: Halogens. Knowledge in Advance: The word ‘helo’ is Greek and having the meaning of ‘salt’. ‘Gen’ means to ‘generate’. The halogens are salt forming elements. These form salts with metals and one non-metal (NH4+ called ammonium ion); for example, NaCl, (sodium chloride is a salt), KBr (Potassium bromide is another example of salt), NH4Cl (ammonium chloride is also a salt).
- 8A: Noble gases.
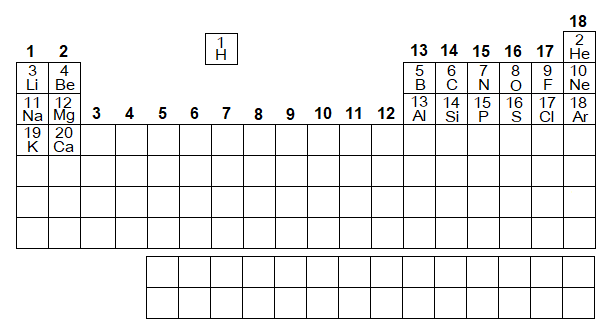
Nowadays, the periodic table is structured into 18 groups; from left, starting from 1 (1A) to 18 (8A) without discrimination of A & B-blocks, as in the following diagram. The hydrogen has been placed a separate position due to its similarities and dissimilarities with alkali metals as well as halogens.
Periods’ Numbers:
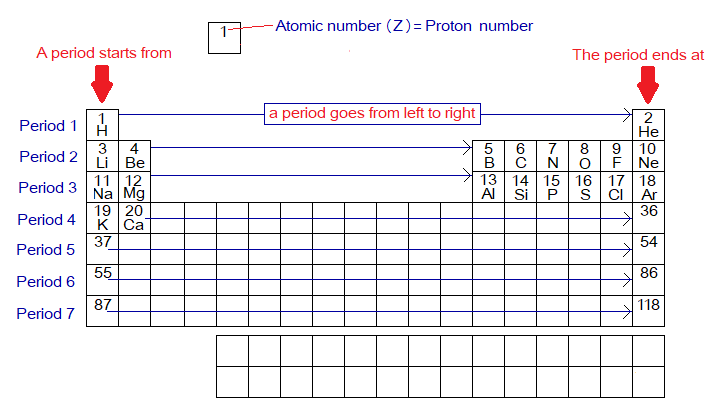
- By definition, the periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table; and containing elements in one-by-one ascending order of their atomic number. The horizontal rows are left to right arrangement of elements.
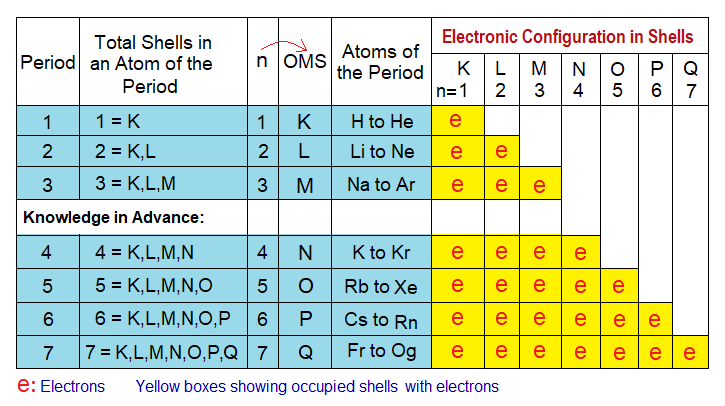
- The periodic table is structured into 7 periods yet.
- The period number corresponds the ‘n’ value, i.e., 1, 2, 3, ….7 of OMS. In other words, what is the number of OMS, that would be the number of periods, as:
Period 1: OMS is ‘K’, and n=1 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 2: OMS is ‘L’, and n=2 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 3: OMS is ‘M’, and n=3 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 4: OMS is ‘N’, and n=4 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 5: OMS is ‘O’, and n=5 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 6: OMS is ‘P’, and n=6 in entire row related to A-block elements.
Period 7: OMS is ‘Q’, and n=7 in entire row related to A-block elements.
So, the period number also corresponds to the total number of occupied shells in atoms of that horizontal row, as elaborated in the table below: