Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Element: definition & introduction
- Compound: definition & introduction
- Molecule, molecular formula
- Di, tri, tetra, polyatomic molecules
- Mixture: definition & types
- Difference between compound & mixture
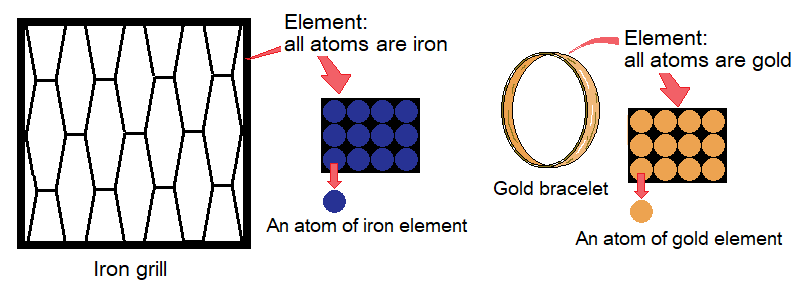
Element: Definition and Introduction
By definition, “an element is a substance made by identical particles”. These particles are called atoms. Different elements have different atoms which are not identical by their structure. For example, iron is an element and all atoms are identical. Gold is another element and its identical atoms are different from iron.
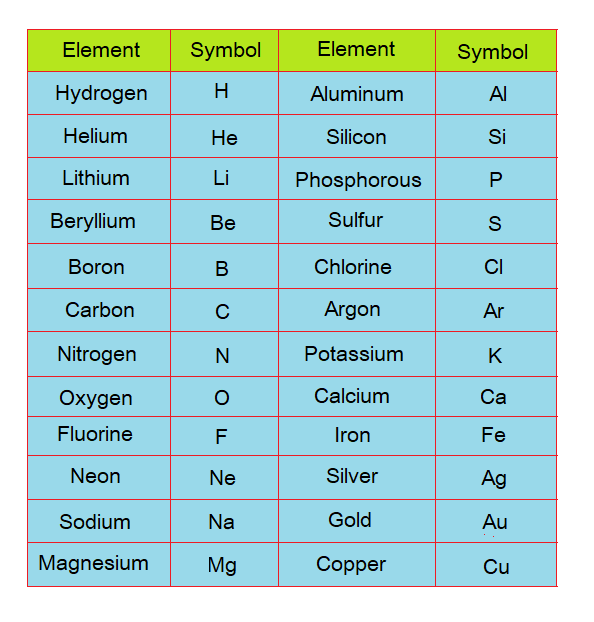
There are total 118 different elements that have been arranged in a periodic table in a particular way; out of which 92 are naturally occurring, while rest of the elements are synthetically produced. Few examples are given in the following table along with their symbols. The elements have given their specific symbols; otherwise, to write their full name each time is a tough job.
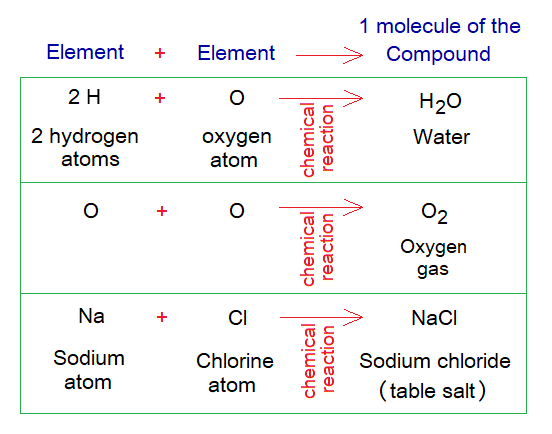
Compounds: Definition and Introduction
By definition, “a compound is a pure substance made by molecules”. For example, water, table salt, oxygen gas, nitrogen gas, carbon-dioxide gas etc. The molecules are formed by the chemical reactions between atoms of elements either similar or different.
Molecule and Molecular Formula:
The molecule is defined as “a smallest unit of the compound, made by more than one atom, either same or different”. The molecules are written by their distinct formula known as molecular formula; also called chemical formula. The formula shows types and number of atoms with their symbols with specific ratio; and it is the simplest form to write the molecule. Each compound has its own molecular formula, like, CO2 for carbon-dioxide, H2O for water, CaCO3 for calcium carbonate etc.; few other examples are given in the table.
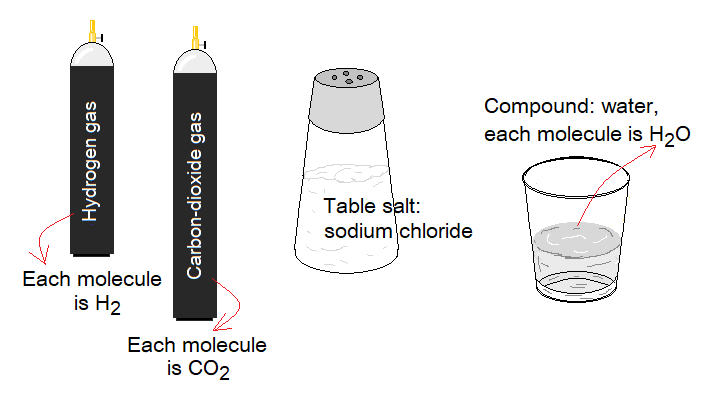
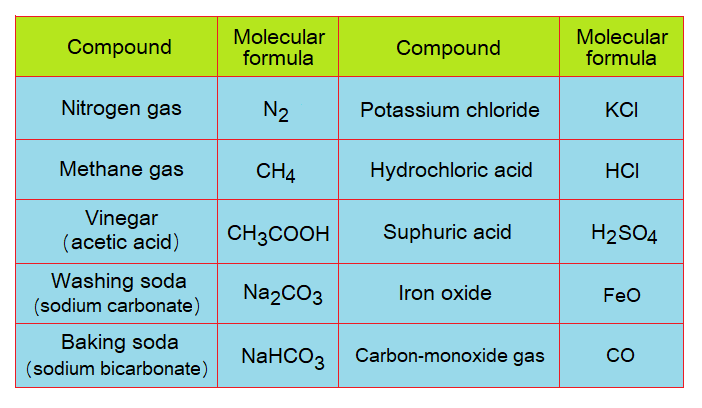
Diatomic, triatomic, tetratomic, polyatomic molecules:
- The molecules formed by the chemical combination of two atoms are diatomic, for example, H2, O2, N2, CO, FeO, KCl, HCl, NaCl.
- The molecules formed by the chemical combination of three atoms are triatomic, for example, CO2, H2O, O3 (ozone), SO2 (sulfur-dioxide gas).
- The molecules formed by the chemical combination of four atoms are tetratomic, for example, NH3 (ammonia gas).
- The molecules formed by the chemical combination of many atoms are polyatomic, for example, CH3COOH, C6H12O6 (glucose).
Mixture: Definition and types
By definition, “a mixture is a physical combination of more than one substance”. It is not a chemical combination as in molecules’ formation. Thus, a mixture is an impure substance. The mixing can occur between any type of state of the matter, as shown in table below:
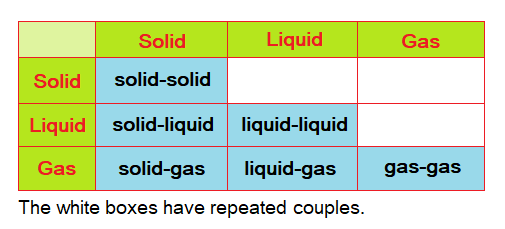
Following table shows few examples related to various categories of the mixtures.

Difference Between Compound and Mixture
| Compound | Mixture |
| The compound is a pure substance formed by the chemical combination of atoms. | The mixture is a physical combination of substances. It is an impure substance. |
| The smallest unit of the compound is a molecule, that has specific ratio between atoms and is written by a specific chemical formula, for example water H2O, oxygen O2. | There is no smallest unit of the mixture, no specific ratio between atoms, no chemical formula. The ratio of the components of the mixture can easily be changed; for example, 5 grams salt in 100 ml water or 10 grams salt in 100 ml water. |
| The atoms of the compounds cannot be separated without chemical processing. | The components of the mixture can be separated by physical means. For example, iron particles present in sand can be separated by using magnet. |
| During chemical combination (chemical reaction) the energy is required or emitted. | Generally, there is no need of energy to mix the substances to form the mixture. However, to form solutions sometimes heating is required. |