Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Introduction of glycidic ester structure
- Synthesis
- Mechanism of the reaction
Introduction:
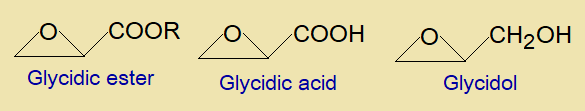
Glycidic ester is an organic compound having two functional groups, epoxide & ester group. In this class of glycidic compounds, not only ester but organic acid group or the hydroxyl groups are also attached with epoxide, forming glycidic acid & glycidol respectively.
Synthesis of Glycidic Ester:
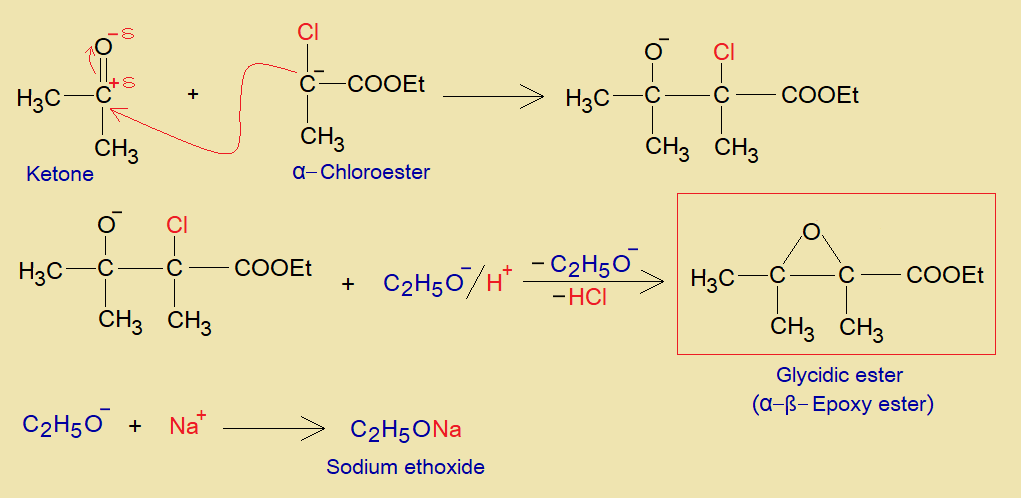
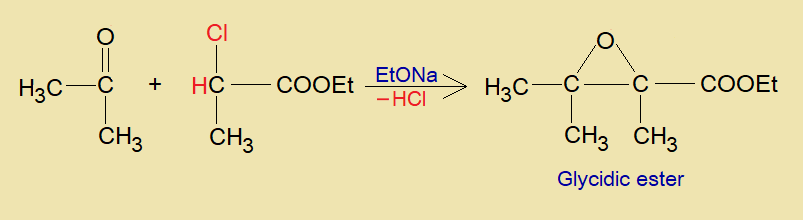
This ester can be prepared by Darzens condensation reaction. The method was developed by a Russian chemist Auguste Georges Darzens (1867-1954) in 1904. In this reaction, aldehyde or ketone reacts with α-haloester in the presence of conjugate base ethoxide (C2H5ONa, aka, sodium ethanolate). Resultantly, glycidic ester is produced.
Mechanism:
- The ethoxide ion acts as a base to cause deprotonation from α-haloester and makes carbanion (an active methylene).
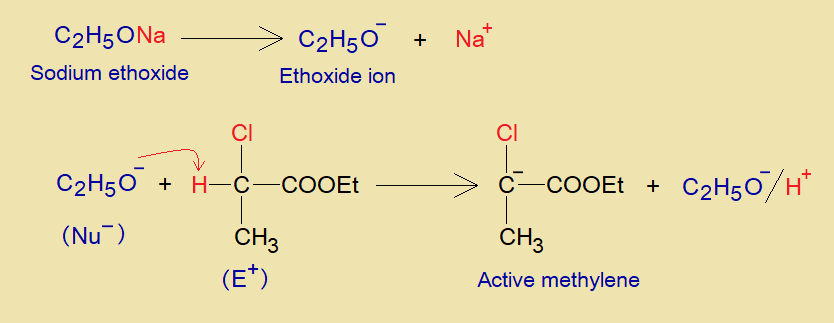
- The carbanion of ester attacks on partial positive carbon of aldehyde or ketone to make a carbon-carbon link, and creates oxyanion (aka, oxoanion).
- Ultimately, by dehalogenation, the α-ß-epoxy ester (a glycidic ester) is formed. These esters have many applications in pharmaceutical industry.