Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition
- Chemical reaction
- Mechanism
Definition:
It is a condensation reaction between two esters to produce beta-diketoester.
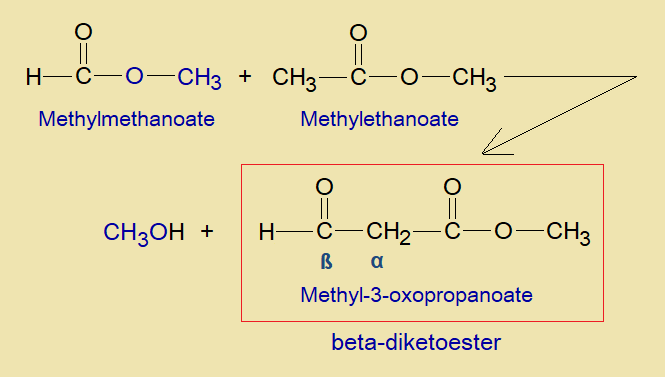
Chemical Reaction: The condensation between two esters, either similar or dissimilar, were reported for the first time by a German chemist Rainer Ludwig Claisen in 1887. The mechanism is a base catalyzed and the final product is beta-diketoester, also called ß-ketoester. For example, a condensation reaction between methylmethanoate (methylformate) and methylethanoate (methylacetate) can yields beta-diketoester (methyl-3-oxopropanoate) and methanol.
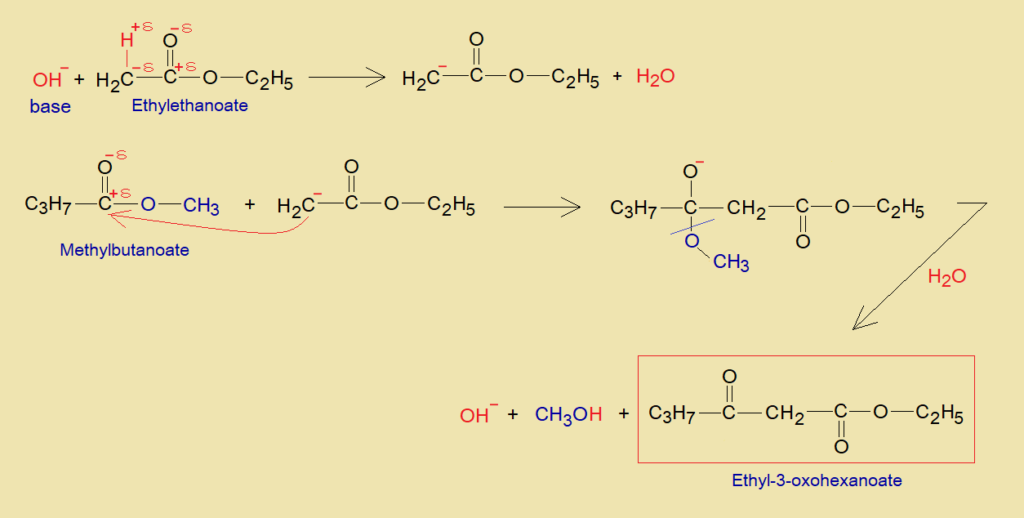
Mechanism:
The detailed mechanism between ethylethanoate and methylbutanoate is given as under:
- Beta-carbon of ethylethanoate acts as active methylene by removing acidic hydrogen in the presence of hydroxide ion of a base; and attains negative charge.
- The carbanion of ethylethanoate establishes a carbon-carbon bond with partial positive carbon of carbonyl of methylbutanoate. Thus, ultimately, the beta-diketo ester (ethyl-3-oxohexonoate) and the methyl alcohol are formed by releasing OH– ion.