Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition of an atom
- Subatomic particles
- Nucleus & shells
- Charges on subatomic particles
- Masses of subatomic particles
Definition of an Atom
By definition, “an atom is a smallest yet invisible unit of an element that can undergo into chemical reactions and is consisted of subatomic particles”.
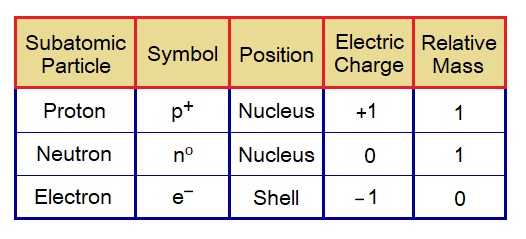
Subatomic Particles:
An atom is consisted of mainly three subatomic particles, these are:
- Proton
- Neutron
- Electron
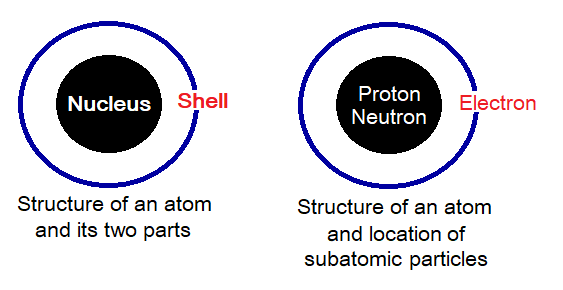
Nucleus & Shells:
The atomic structure is consisted of two parts, nucleus and the shells, the locations of subatomic particles. Nucleus is a central (inner) part of the atom and is consisted of neutrons and protons. The shells are the imaginary paths (outer part) around the nucleus where the electrons revolve; in other words, the electrons revolve around nucleus. The shells are also called orbits. The particles that exist in nucleus are called nucleons and obviously these are protons or neutrons.
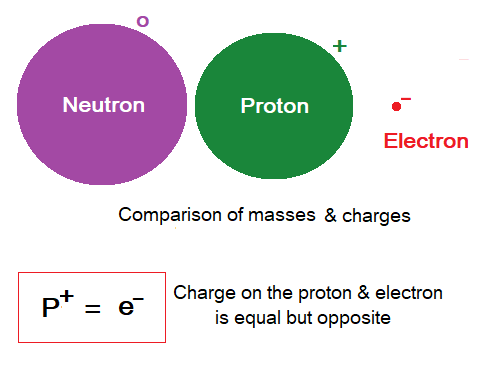
Charges on Subatomic Particles:
- A proton is positively charged particle. Its symbol is p+.
- An electron is negatively charged particle. Its symbol is e–.
- The neutron is neutral having no charge, neither positive nor negative. Its symbol is n°.
- The charges on proton and electron are equal but opposite. Proton carries 1 positive electric charge and electron carries 1 negative electric charge.
- These charges are the symbols as similar charges repel each other; while opposite charges attract each other. Electrons had been given symbol negative; while proton positive. Now, all the available literature reports as such and cannot be changed. In other words, if electron was given positive while proton the negative symbols then it was practical.
Masses of Subatomic Particles:
- A proton is 1836 times heavier to an electron by its mass. Its mass is written as 1.
- An electron is 1836 times lighter than the mass of a proton. Its mass is written as 0 (zero) due to negligible as compared to proton.
- The neutron is 1839 (also reported even to the number 1842) times heavier to an electron by its mass; while just a little bit heavier than a proton. So, its mass is also written as 1.