Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Metallic bond: definition
- Electronic cloud
- Metals are conductors
- Metals are malleable
- Metals are ductile
- Abundance of metals
Metallic Bond:
Definition: “The type of chemical bond in metals where the valence electrons are delocalized to move freely between cationic atoms; resultantly electrostatic attractive forces are created between oppositely charged particles”.
Electronic Cloud:
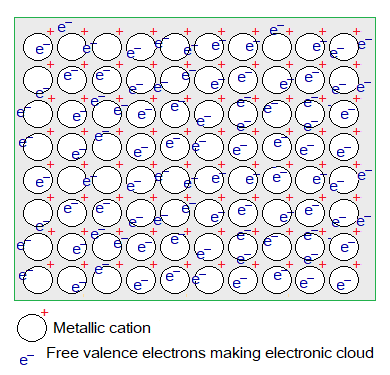
The sea of electrons is another term used for electronic cloud. The electrons of the outermost shells are called valence electrons. These establish a loose bonding and do not stay in their own shells but escape. So, an electronic cloud is formed by these delocalized electrons. Resultantly, neutral atoms gain positive charge. It is the property of metals to lose electrons to form cations, and is called electropositive behaviour.
An electrostatic force is established between delocalized electrons and the cations. This is called metallic bond. But these electrons do not stay long at a particular atom; stay for a while and again escape to go to another atom. This is a recurring phenomenon.
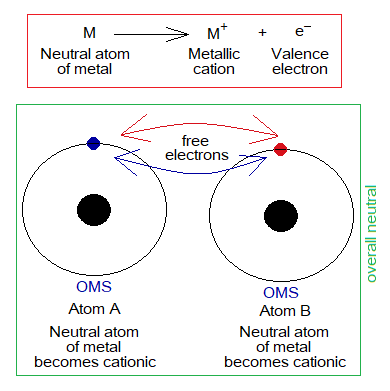
Based on the following figure, it can be interpreted in a simple way. Suppose, there are just two atoms, each containing 1 valence electron. Both electrons escape and cause to form cations. Now, both electrons move here and there among two cations and could maintain their temporary stay with anyone of them; then move away for another stay anywhere else. These are not localized and bound to any particular atom but are delocalized like a stray animal. This phenomenon occurs consistently, making a metallic bond by electrostatic forces of attractions.
Metals are Conductors:
- All metals are good conductors of electricity. This property is due to the availability of free electrons to cause electric current to flow.
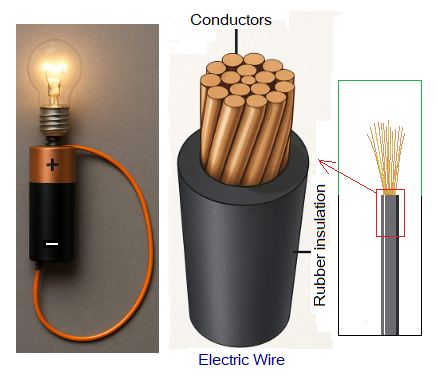
- All metals are good conductor of heat due to the same reason of having free electrons to move throughout the metallic material. These electrons absorb heat and kinetic energy increases. So, they move fast; consequently, transfer the heat throughout. When we touch a metal gate in bright sunlight in summer, it gives feeling of burning. And when we touch it in winter nights, it feels cool.

Metals are Malleable:
The word ‘malleable’ has its Latin origin from ‘malleus meaning hammer’. So, malleable is used for the metals to be hammered. The metals can easily be hammered to change their shape into sheets, also can be rolled but do not crack. Their sheets can be cut with scissor. The layers of metals’ atoms can slide over by hammering and change into thin layers, as shown in the figure.
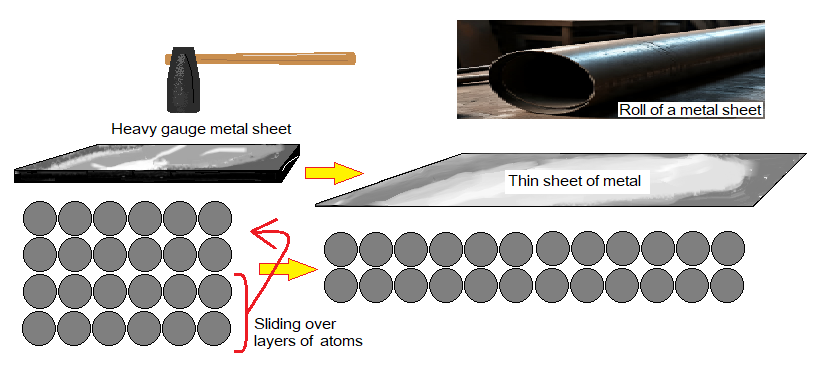
Metals are Ductile:
Mostly, the metals are flexible and can easily be molded into any kind of desired shape. So, these are used to make long wires. Thus, this property makes metals ductile. This term ductile has the meaning ‘can be drawn into any shape without breaking’.

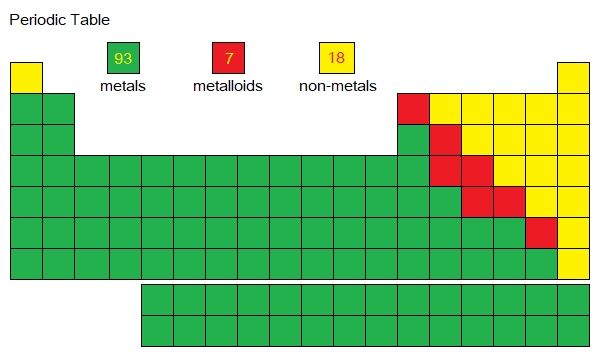
Abundance of Metals:
Metals are abundant on the earth. Task: From the following boxes, calculate in percentage the metals, semi-metals (metalloids) and non-metals. Semimetals are the elements having their properties intermediate between metals and non-metals (not discussed here).
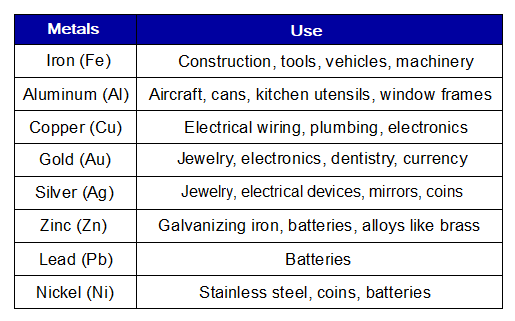
Metals are very useful elements in our lives. Few selected examples and their uses are given in the following table.