Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Crystal lattice: definition
- NaCl crystal lattice and unit cell
- Melting point of ionic compounds
- Boiling point of ionic compounds
- Electrical conductivity: an example of molten-NaCl electrolysis
Crystal Lattice :
Definition: “The particles of crystalline solids exist in symmetrical arrangement of three-dimensional repeating pattern called crystal lattice”. Lattice means a ‘grid’.
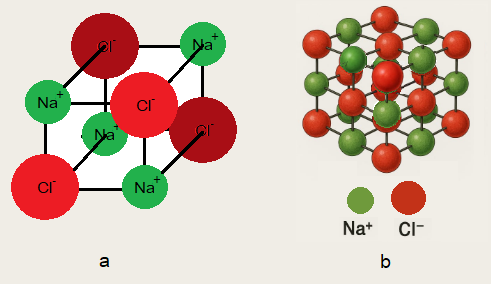
NaCl Crystal Lattice and Unit Cell:
Sodium chloride occurs naturally as ‘rock salt’, also known as ‘halite ore’, as shown in picture below.

It is a crystalline solid and exists as ‘cube’ by the arrangement of particles. There is an alternative arrangement of Na+ and Cl– ions in the cube.
A unit cell can be defined as “the smallest unit of a crystal that carries all the features of a crystal in three-dimensional arrangement”. NaCl has its unit cell a cube that carries cations and anions at all of its corners with alternative arrangement, as shown in the diagram a. The eight-unit cells together form a smallest crystal lattice as shown in the diagram b.
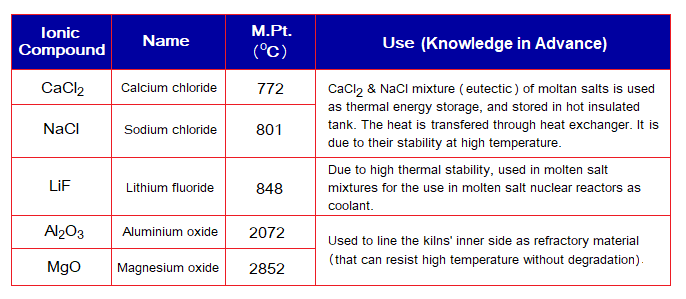
Melting Points of Ionic Compounds:
The electrovalent (ionic) bonds have their melting points high due to the reasons:
- Electrostatic forces of attractions between cations and anions.
- Crystal lattice formation. The molecules are not independent as covalent but cluster of ions. For example, NaCl is not 1 Na+ and 1 Cl– ion but a cluster of ions. So, their whole number ratio is determined that is the chemical formula of a particular compound, go to the link: https://chemiologist.com/understanding-ionic-bonding-through-common-examples/
- This reason rises up their melting points so high.
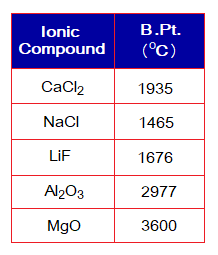
Boiling Points of Ionic Compounds:
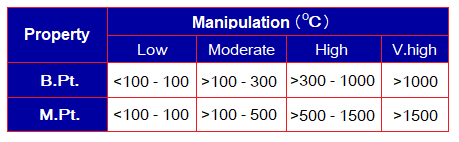
Since their melting points are higher, the boiling points will also be higher due to strong attractive forces between cations and anions; as shown in the following table:
To classify melting and boiling points as low, moderate, or high, a general guideline has been manipulated in the following table.
Electrical Conductivity
Definition: “It is the property of a material to conduct an electric current” It is also called specific conductance.
Electrical conductivity can be measured in three states of a substance:
- In solid state
- In molten state
- In aqueous solution state
The ability of a substance to allow electric current pass through it might be different in its different states, as shown in the following table:
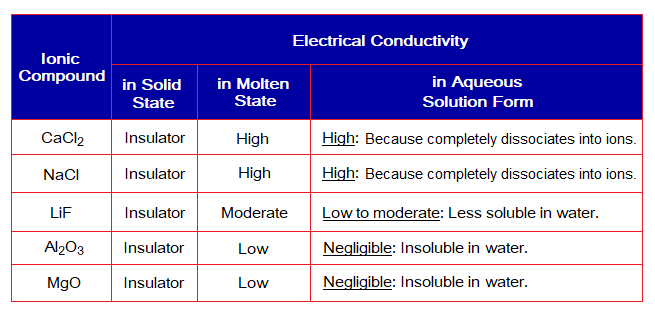
Ionic compounds don’t conduct electric current in solid state. Because, there is no mobility in their ions that is the first condition for this property. However, in molten state (liquid), and in aqueous solution state the mobility of ions is possible and electrical conductivity is doable. The greater is the ions splitting, higher the mobility and consequently greater will be the conductivity.
In the following diagram, solid NaCl is heated to get its molten state; then electric current is passed through. Because, the ions can move in liquid state, thus, the free and directionless mobility without electric current is thereafter aligned according to the terminals of the battery by the following way:
- The positive ions (Na+) called cations move towards cathode (negative electrode); and accumulate there.
- The negative ions (Cl–) called anions move towards anode (positive electrode); and gather there.
- During this process, the chemical reactions take place, and new products are formed, the sodium metal and the chlorine gas. The metal is obtained as liquid at the first then solidified; while the chlorine is collected in gaseous state.
- This is an overall reaction; but it takes place in several steps as shown below. Chlorine anions undergo into a change at anode by losing electrons, called oxidation. And ultimately two chlorine neutral atoms establish a covalent bond to form chlorine gas (Cl2).
- Sodium cations at cathode undergo into a change by gaining electrons (coming from Cl– anions, and neutralize into molten sodium metal. This step is called reduction. The electrons from the anode electrode travel outside the cell through a wire and re-enter into the cell via the cathode in DC current.
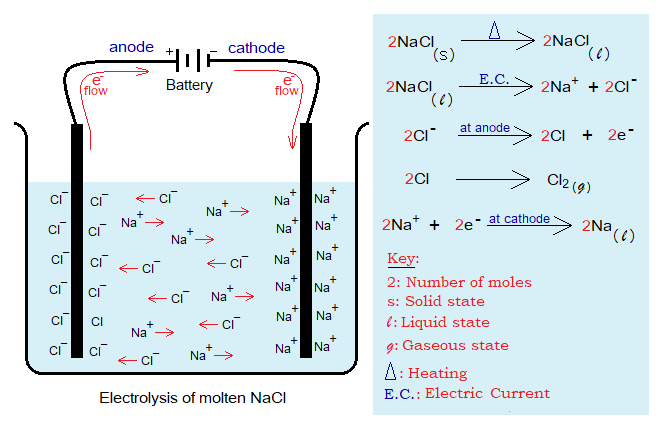
- This process is called electrolysis. For NaCl-electrolysis the method is called Downs’ cell and developed by an American chemist James Cloyd Downs in 1923. The cell is not so simple in its design as shown above. By definition, “the electrolysis is an electrochemical process for decomposing ionic compounds and obtaining new products by passing electric current through them in electrolytic cell”. So, in other words, it can be said that NaCl electrolyzed into Na metal and Cl2 gas.