Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
Contents:
- Noble gases and their position in periodic table
- Electronic configuration of noble gases
Noble Gases and their Position in Periodic Table:
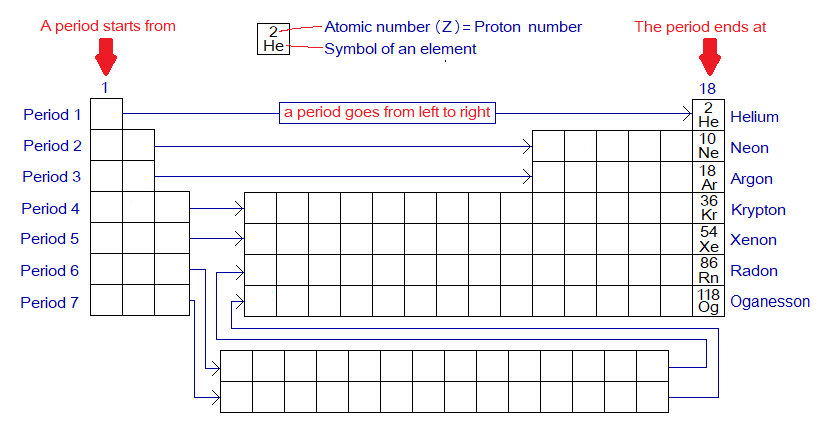
Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon & oganesson are seven known noble gases and aka inert gases. These are placed at extremely right column (18th) of Moseley Modern periodic table, https://chemiologist.com/atomic-number-and-its-use-in-periodic-table/ . In other words, each period of the periodic table ends at a particular noble gas as shown below. A summary of the noble gases is shown in the following diagram of periodic table. Each period starts from left side and ends at right side to the noble gas.
- Period 1 ends at He.
- Period 2 ends at Ne
- Period 3 ends at Ar
- Period 4 ends at Kr
- Period 5 ends at Xe
- Period 6 ends at Rn
- Period 7 ends at Og
Electronic Configuration of Noble Gases:
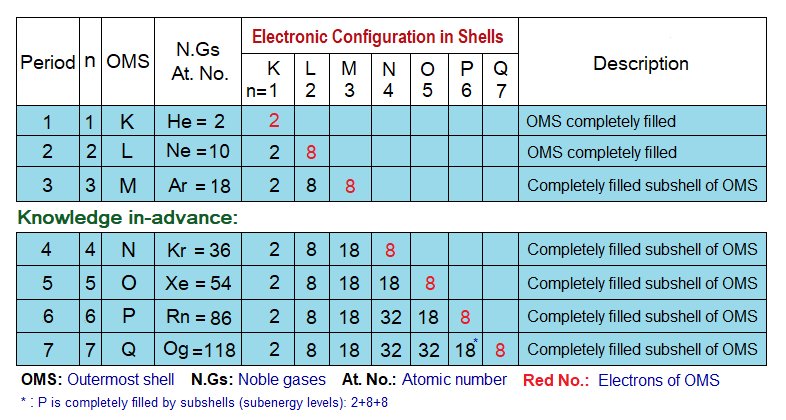
The noble gases are the only elements having their atoms with stable electronic configuration due to completely filled outermost shell (OMS) among helium and neon; while completely filled subshells of OMS among argon, krypton, xenon, radon & oganesson.
Knowledge in Advance:
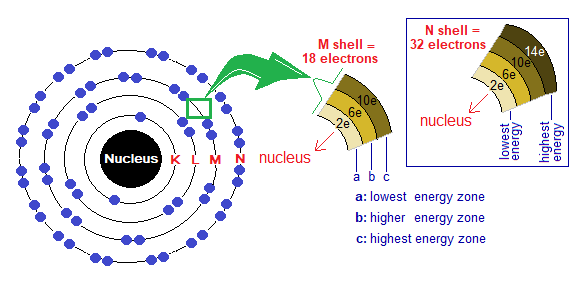
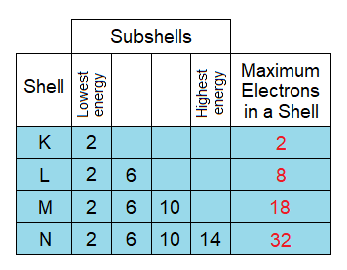
- The shells do not have single energy level; but divided into different energy zones from lowest to highest, called sub-energy levels or subshells. For example, the M-shell has three energy zones from lowest to highest as shown below. The lowest energy zone always stays towards nucleus and vice versa. The filling of electrons follows the ascending order according to energy levels of the shell. First, lower energy zone is filled, then the next middle one and finally the highest energy zone. Lowest always holds the capacity of maximum 2 electrons, the next one 6 electrons and the third one 10. So, by that way, M-shell can accommodate a total of 18 electrons.
- Oganesson is a new and most recently discovered synthetic element named in 2016 upon the name of Yuri Tsolakovich Oganessian (date of birth 1933, alive in 2025), a Russian nuclear physicist. Oganesson is the heaviest known element among all by today’s date; having mass number 294 and atomic number 118 (e=p=118; n=176). By appearance, it is a solid. It is still the last element of the periodic table.
The electronic configuration of noble gases is given in the following table. First K shell is filled, then L and then electrons move towards M,N,O,P & at the end towards Q. By the link, look over the four points to know pattern of electrons’ distribution in shells, https://chemiologist.com/electronic-configuration-of-shells-k-l-m-n/ .
- K-shell has the capacity to accommodate maximum 2 electrons. Thus, by that way, Helium (He) has its K-shell completely filled due to 2 electrons of the atom.
- L-shell has the capacity to accommodate maximum 8 electrons. Thus, by that way, Neon (Ne) has its L-shell completely filled. Due to 10 electrons in a total; the distribution is adjusted by 2 electrons in K; which 8 in L-shell.
- From argon to onwards, the subshells of OMS are completely filled, to give a stable electronic configuration to these atoms.
The electronic configuration is written by the following way with respect to distribution among shells.
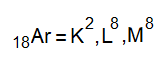
Exercise 1:
- Learn electronic configuration of He, Ne and Ar and learn how to write.
- Learn how the OMS or subshell of OMS is considered ‘completely filled’ by electrons, so that to say the ‘stable electronic configuration’ of noble gases.
Knowledge in Advance:
- The noble gases are also called “inert gases”; because, they are non-reactive (inert: antonym of reactive) in chemical reactions due to stable electronic configurations. The noble name is also given to them due to inertness. Usually, they are inert, but show certain reactions in special conditions.
- The “aerogens” is another name of noble gases. The word has its Greek origin ‘aero’ means ‘air’ and the suffix ‘gen’ means ‘to produce’. Because, these are naturally occurring gases in air, thus, called aerogens, i,e., ‘air-born’.