Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Rate of diffusion and molecular mass
- Experimental verification
- Chemical reaction
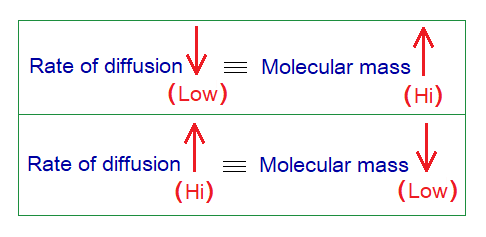
Rate of Diffusion and Molecular Mass:
The diffusion in gases is at higher rate as compared to liquids and solids. However, different gases have different rates of diffusion. This rate (speed) depends upon molecular masses of the gases. Higher the molecular mass of a gas, slow will be its rate to diffuse; and vice versa.
Experimental Verification:
Take a long glass tube, plug it’s both ends with cotton soaked in concentrated solutions of hydrochloric acid and ammonia. At one end cotton plug soaked in one solution and at the other end soaked in second solution. Soon, there will be appeared white fumes inside the tube more towards the end nearer to hydrochloric acid cotton plug, as shown in the following diagram.
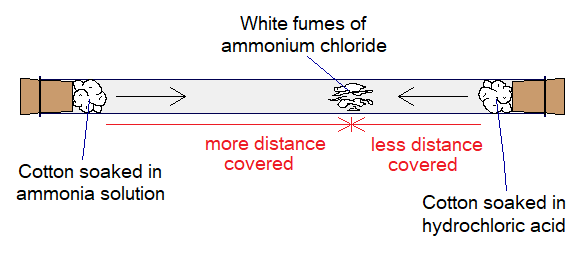
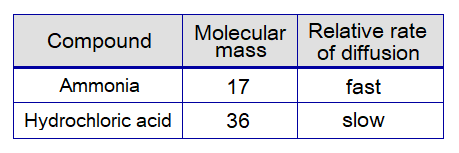
The molecular mass of ammonia is 17 much smaller than 36 of hydrochloric acid. Thus, rate of diffusion of ammonia is faster relatively. So, the fumes of ammonia move faster towards the other end; while, hydrochloric acid fumes move relatively slow towards the opposite end.
Chemical Reaction:
When both fumes meet on the way, the white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed due to chemical reaction between two. As stated, these fumes are formed more nearer to the end of hydrochloric acid cotton plug.