Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Higher Education Department, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Matter & mass
- Properties of matter – definition
- Properties of solids
- Properties of liquids
- Properties of gases
Matter: Anything that covers space due to its existence and has its mass. Mass is the quantity (amount) of the matter, e.g., 250 grams apples, 1-kilogram potatoes etc.
Properties of the Matter – Definition:
The characteristics that can be observed and measured are called properties of the matter. These can be chemical as well as physical. Solids, liquids and gases are three states of the matter and have their distinguished properties.
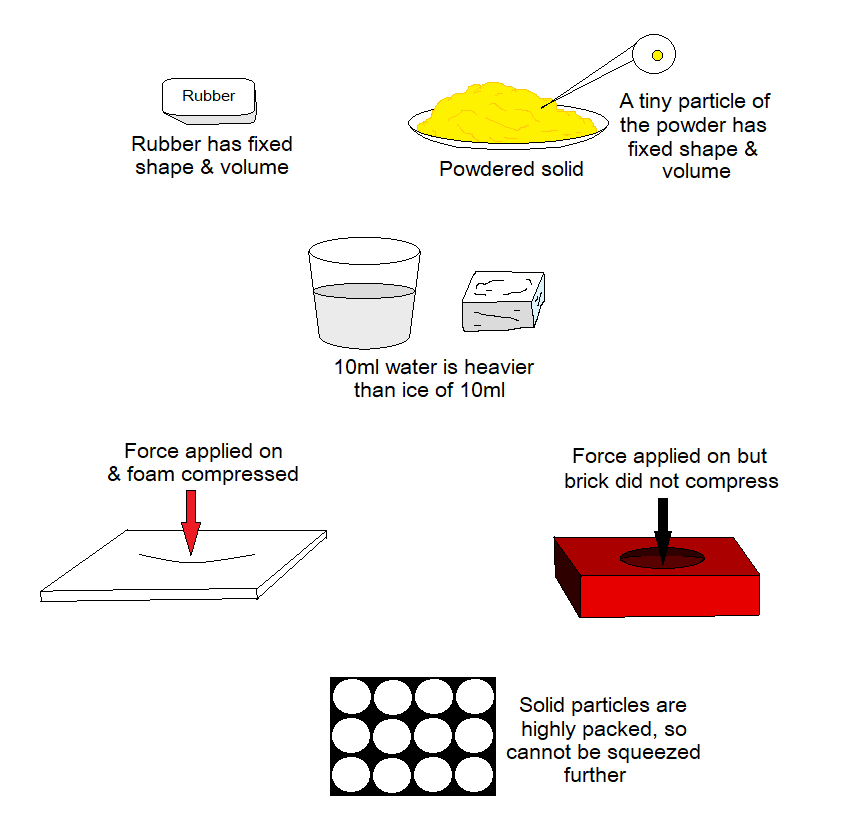
Properties of Solids:
- Shape: They have fixed (definite) shape. The powder can change the shape of the container, but, its tiny particle is considered as having the fixed shape.
- Volume: They have fixed volume.
- Density: By a general trend, the solids have their density higher as compared to liquids and gases. But the fact doesn’t true always, because there are exceptions, like water has higher density than ice. So, ice cube floats on the surface of water. Density is mass per unit volume (d=m/v). On the same volume, if the substance has its mass greater than the other then its density will also be greater.
- Compressibility: Solids are compact and cannot be compressed. However, some solids can be compressed due to having their porous and soft nature, like foam sheets. Although, a brick is porous, but it is not soft as a foam.
- Squashing: Because, the particles of the solids are highly packed, so, they cannot be squeezed by applying force.
- Flow: The solids cannot flow like liquids and gases. Their particles have stronger attractive forces, so, these cannot flow from their fixed positions.
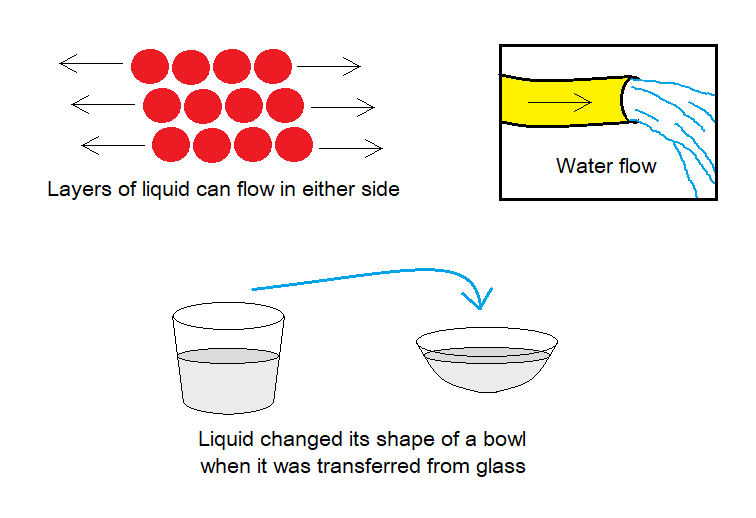
Properties of Liquids:
- Shape: They don’t have fixed shape; and can change the shape of the container.
- Volume: They have fixed volume like solids.
- Density: The liquids have lower density as compared to solids but higher than gases. Density of water is higher than ice as described above.
- Compressibility: Like solids, the liquids cannot be compressed. Because, their particles are compact. In other words, there is no more space between particles to be compressed more; however, a little bit, almost negligible, change appeared on high pressure and low temperature.
- Squashing: Because, the particles of liquids are packed and having no space to squeeze further, so, they do not show the property of squashing at applied force.
- Flow: Unlike solids, the liquids can flow. They can be poured from container to container easily. Although, their particles are compact but have relatively less attractive forces between as compared to solids; so, the layers can flow and cause the liquid to flow.
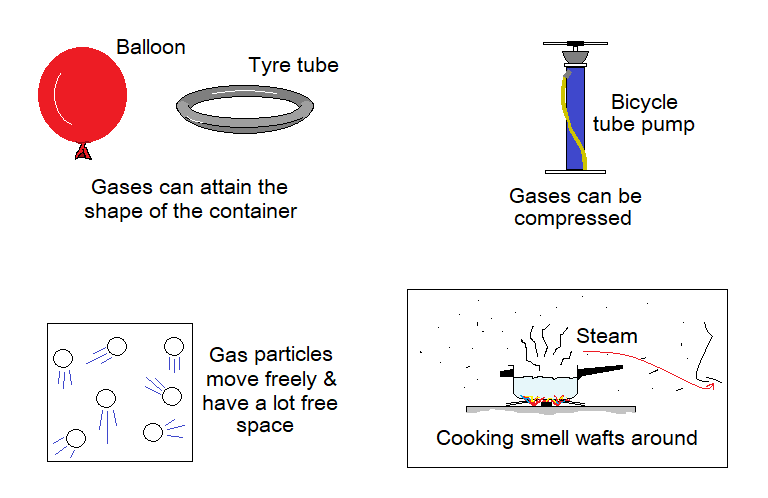
Properties of Gases:
- Shape: They don’t have fixed shape; and can change the shape of the container.
- Volume: They don’t have fixed volume like solids and liquids. They attain the volume of the container.
- Density: The gases have lower density as compared to solids and liquids.
- Compressibility: Unlike solids and liquids, the gases can be compressed. Because, their particles are far away from each other and having a lot of space between.
- Squashing: As stated, that the particles of gases are far away from each other and having a greater space to squeeze further, so, they show the property of squashing at applied force.
- Flow: Like liquids the gases can flow. Few gases like carbon-dioxide can be poured from one container to the other.