Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition
- Introduction of ylide
- Mechanism of synthesis
Definition:
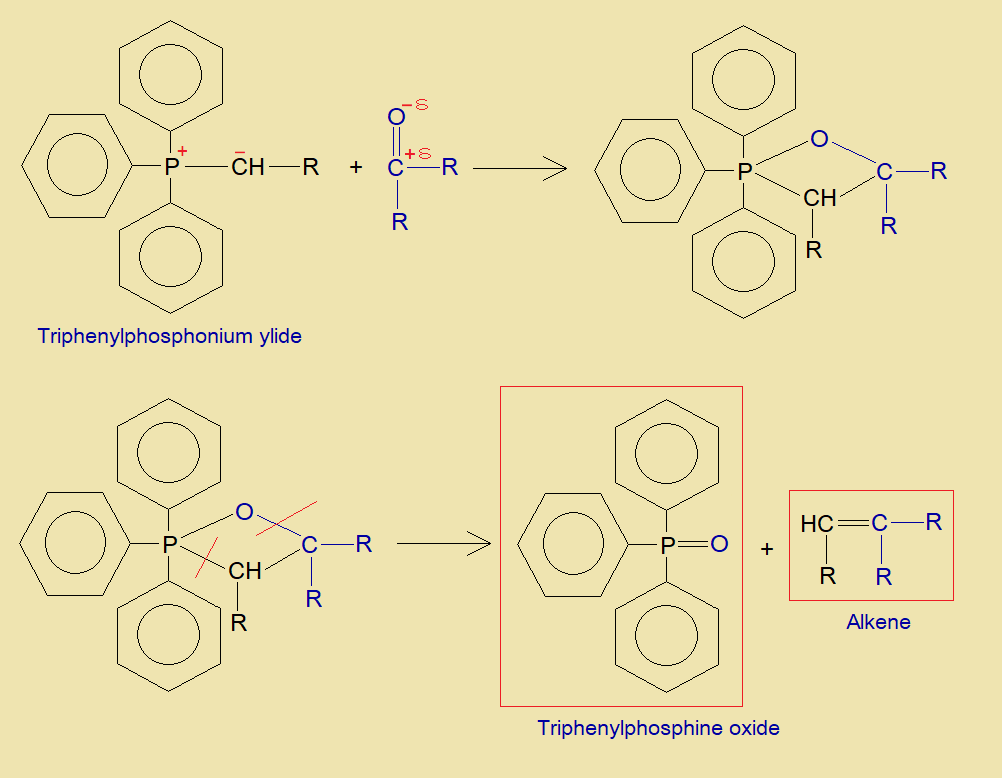
It is a condensation reaction between aldehyde or ketone with triphenylphosphonium ylide to yield triphenylphosphine oxide and alkene.
Introduction of Ylide:
This reaction was developed by a German Chemist George Wittig (1897-1987); who was awarded Nobel prize in chemistry in 1979 for his discovery.
Ylide are the organic compounds having positive as well as negative charges, making the molecule overall neutral; in other words, these are dipolar neutral molecules. Ylide etymology is a combination of -yl and -ide. The ‘-yl’ is for organic radical (e.g., alkyl radical of alkane), and the ‘-ide’ is for ionic nature (e.g., iodide). Ylide belongs to zwitter ion classification as well.
Mechanism of Synthesis:
- The carbanion (active methylene) of triphenylphosphonium ylide makes a carbon-carbon linkage with partial positive carbonyl-carbon of aldehyde or ketone. And the positively charged phosphorus makes a bond with carbonyl-oxygen due to its partial negative character. Thus, a four membered ring is formed as shown below.
- Ultimately, the rings breaks from two sides to produce alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide.