Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Department of Higher Education, Govt. of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition and synthesis
- Alkylidene introduction
- Mechanism
Definition and Synthesis:
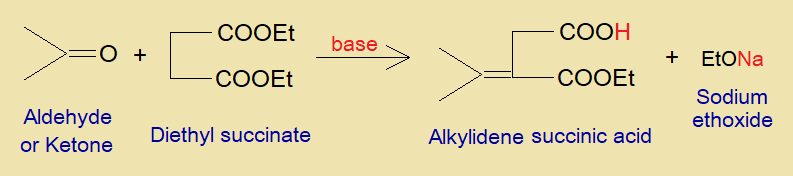
It is a condensation between aldehyde or ketone and the ester of succinic acid to produce alkylidene succinic acid. This reaction was developed by a German chemist Hans Stobbe (1860-1938).
Alkylidene Introduction:
When two hydrogen atoms are removed from the same carbon atom of alkane to produce a divalent functional group is called alkylidene radical group of organic compounds; that then makes a double bond with another molecule, as in the example of alkylidene succinic acid.
Mechanism:
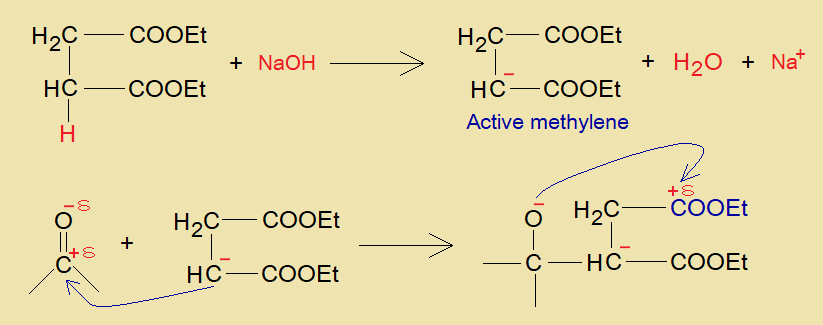
- One of the alpha-carbon of succinic acid makes carbanion with a base, that acts as active methylene compound.
- The carbanion makes a carbon link with partial positive carbonyl-carbon of aldehyde or ketone; consequently, a negative charge is carried by the carbonyl-oxygen.
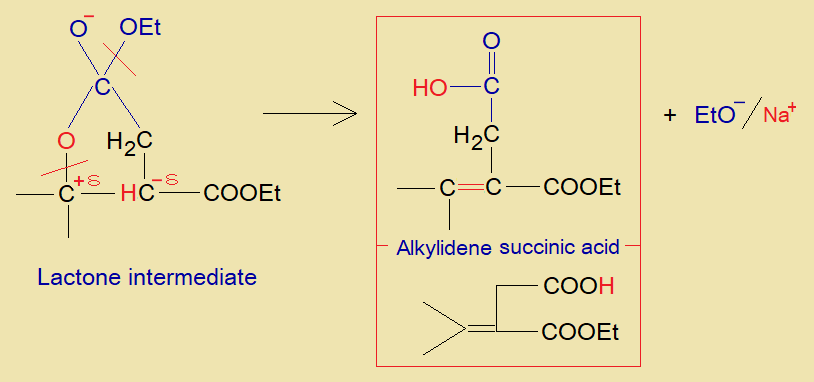
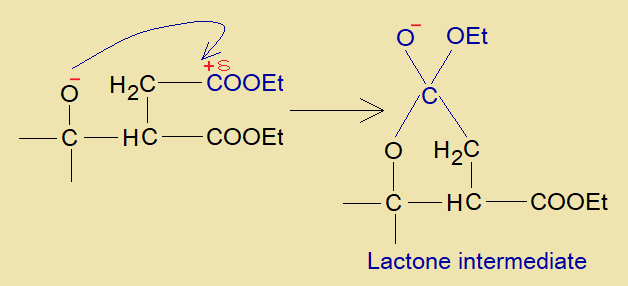
- The oxyanion (aka, oxoanion) makes a linkage with partial positive carbon of ester group to form a five-membered ring (4-carbon, 1-oxygen – a cyclic ester called lactone). This is lactone intermediate.
- The ring is broken by oxygen-carbon bond cleavage. Hydron is removed from alpha-carbon of ester group and shifts towards oxygen to make hydroxyl group.
- Alpha and beta carbon make double bond and ultimately, alkylidene succinic acid is formed.
- The ethoxide ion forms sodium ethanolate.