Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Higher Education Department, Govt. of the Punjab, Pakistan.
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition
- Etymology of aldol
- Synthesis
- Mechanism of aldol condensation
- Base catalyzed
- Acid catalyzed
- Aldol condensation between an aldehyde & ketone
Definition:
An organic compound containing two functional groups, hydroxyl and aldehyde, is called aldol. The synthesis of aldol by the condensation between aldehydes, aldehyde and ketone and even self-condensation in ketones is called aldol condensation.
Etymology of Aldol:
As shown in the figure below, an aldol is a combination of ‘ald’ from aldehyde and ‘ol’ from alcohol, because of the presence of two functional groups as stated above.

Synthesis:
It is a condensation reaction between two aldehydes; these might be similar or dissimilar. However, the main condition of the chemical change depends upon the presence of alpha-hydrogen at least at one of the reactants.
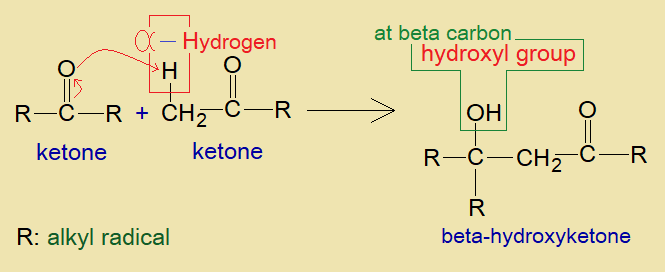
As the formaldehyde (methanal, HCHO) does not carry alpha-hydrogen, so, does not undergo into self-condensation. However, any other aldehyde, such as, acetaldehyde (ethanal, CH3CHO) carries alpha-hydrogen and thus can show aldol reaction with formaldehyde.

Similarly, two similar aldehydes can make aldol product by self-condensation. Likewise, an aldehyde and a ketone also show the same mechanism of the chemical change.
Mechanism of Adol Condensation:
There are two types of mechanisms: base catalyzed and acid catalyzed, as described below.
a. Base catalyzed:
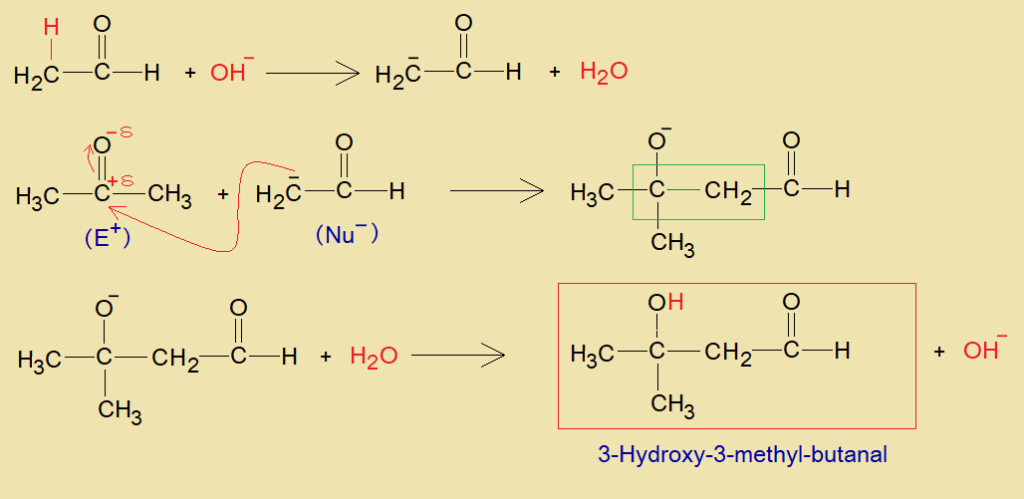
The base (alkali) provides hydroxide ion (OH–) that makes water with hydron (alpha-hydrogen) of aldehyde. Thus, alpha-carbon generates carbanion, a nucleophile; which attacks on partial positive carbon of carbonyl belonging to another aldehyde or ketone. This makes a carbon-carbon linkage that ultimately yields aldol with hydron to form hydroxyl group as shown in the mechanism. Thus, hydroxide ion of the base is recovered ultimately.
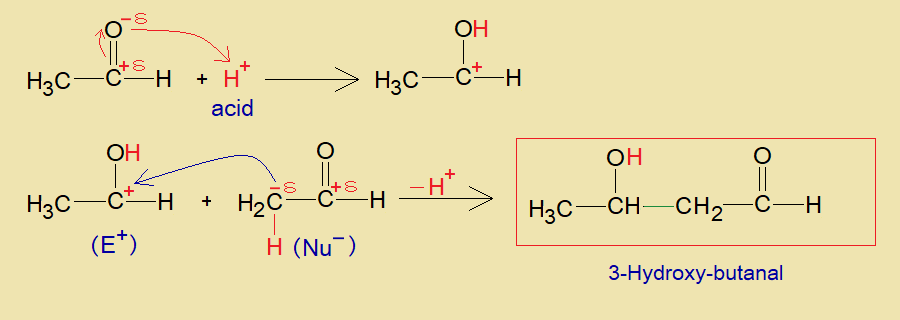
b. Acid Catalyzed:
The acidic hydrogen of an acid makes hydroxyl group with oxygen of carbonyl and generates carbon-cation at aldehyde, and acts as electrophile (E+). This carbon-cation makes a carbon-carbon linkage with partial negative alpha-carbon (nucleophile, Nu–) of another aldehyde molecule and yields aldol. Resultantly, the alpha-hydrogen is removed as proton at the end, as shown in the mechanism.
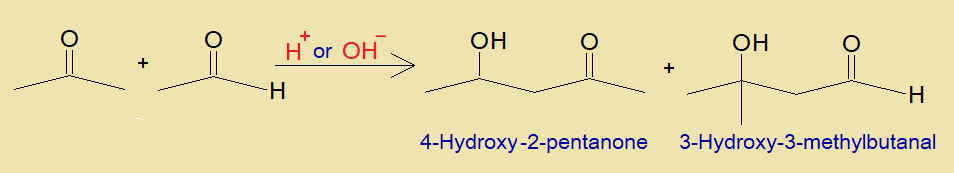
Aldol Condensation between an Aldehyde & Ketone:
Although, the mechanism is same, however, the end products expected different, i.e., 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutanal and 4-Hydroxy-2-pentanone respectively by the aldol condensation between acetone and acetaldehyde.