Mechanism of Chemical Change
Dr. Mudassar Altaf, Associate Professor, Department of Higher Education, Government of the Punjab, Pakistan
The copy of the content is not allowed
Contents:
- Definition
- Overall reaction
- Mechanism of chemical change
- A brief account of the chemicals
Definition:
The addition of an acyl group (RCO-) to methylene (-CH2-) of an active methylene compound is called acylation.
Overall Reaction:
A general view of acylation reaction is shown as under.
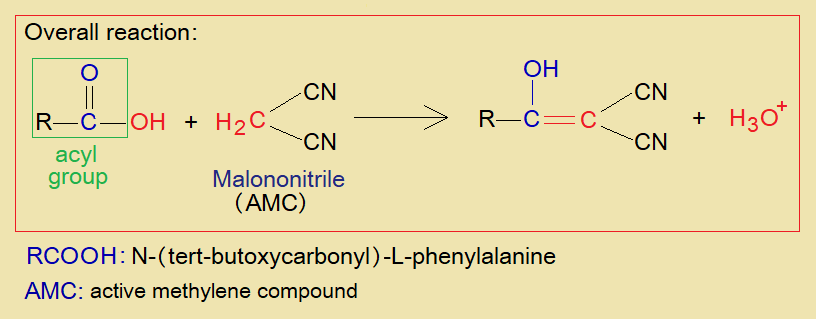
N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine [N-(t-Boc)-L-Pa] is acyl group bearing compound that can undergo into acylation with malononitrile – an active methylene compound. Consequently, a carbon, carbon double bond is formed between two compounds. A detailed mechanism is given here.
Mechanism of Chemical Change:
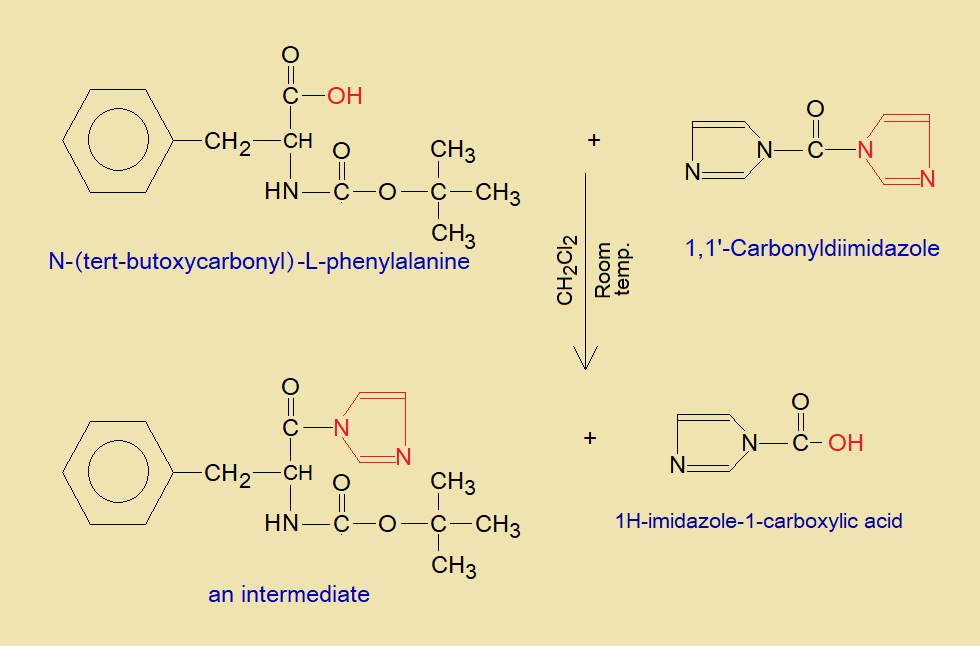
- N-(t-Boc)-L-Pa first of all reacts with 1,1’-Carbonyldiimidazole to form an intermediate molecule. The reaction takes place in methylene bichloride (or dichloromethane CH2Cl2) solvent. Imidazole replaces hydroxyl group of N-(t-Boc)-L-Pa by making a single covalent bond between N of imidazole and carbon of carbonyl of Pa, and an intermediate compound is produced. Further, 1H-imidazole-1-carboxylic acid is also formed.
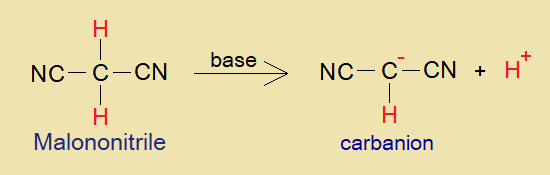
- In the presence of base, malononitrile loses its acidic hydrogen (H+) and carbanion is formed that plays its role as active methylene compound.
- The intermediate of N-(t-Boc)-L-Pa reacts with carbanion of malononitrile and acylation takes place. The carbon-carbon sigma bond is formed by substituting imidazole as zwitter ion which ultimately forms imidazolinium salt with chloride.
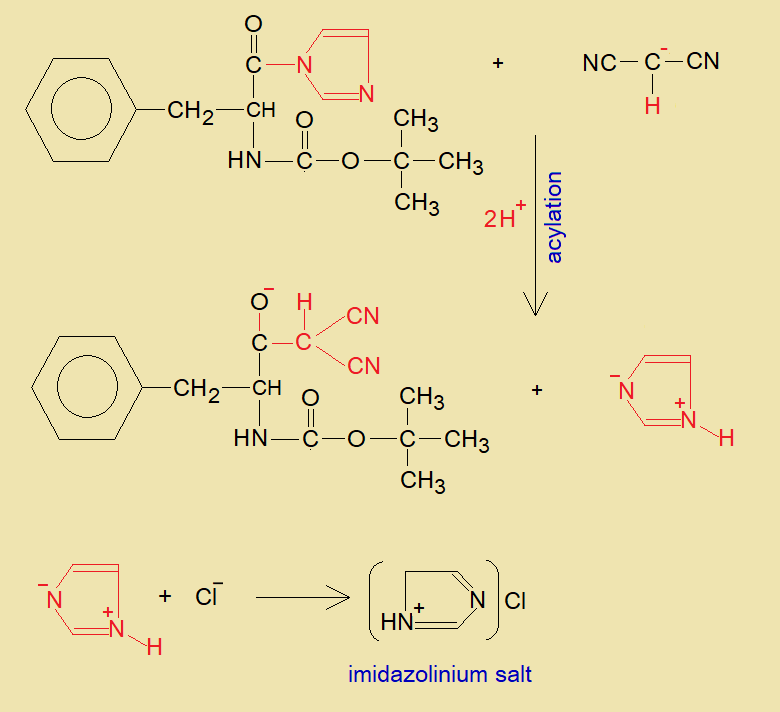
- Hydrogen of dicyanomethylene group (red) shifts to oxide ion of the carbonyl and makes hydroxyl group, thus, unsaturation occurs between carbon-carbon bond in the final product, shown below.
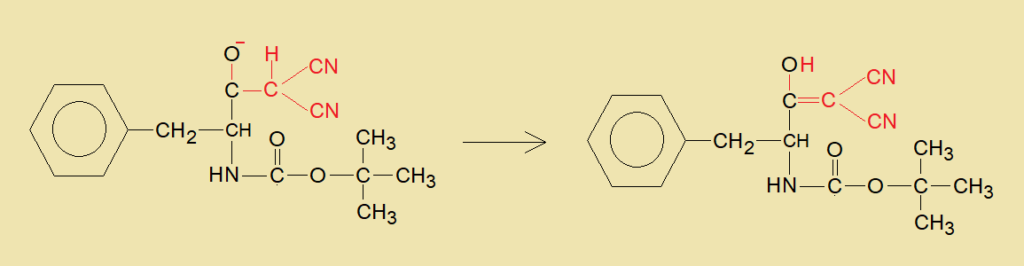
A Brief Account of the Chemicals:
The name Malononitrile is derived from malonic acid [CH2(COOH)2] that occurs in fruits, wheat and vegetables. Melon is a Greek word, meaning apple. Malononitrile is a white crystalline powder, having m.pt. 32°C. It is widely used in pharmaceutical industry. The other names of malononitrile are propanedinitrile, dicyanomethane, malonodinitrile.
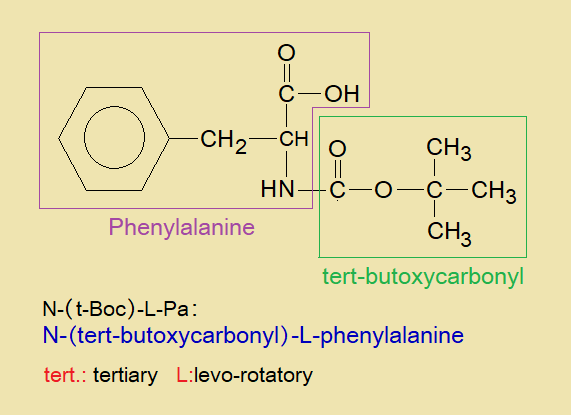
N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine consisted of phenylalanine and tertiary butoxycarbonyl. Phenylalanine is an amino acid to which tert-butoxycarbonyl is bonded with its nitrogen of amine group by means of carbonyl group as shown in the figure. L stands for levorotatory. N-(t-Boc)-L-Pa is a white solid having melting point 86°C.
1,1’-Carbonyldiimidazole is a white crystalline powder, having m.pt. 119°C. Among other names, CDI or N,N’-carbonyldiimidazole are common.



